Once you purchase cryptocurrency, you can trade it or hold on to it hoping for future appreciation in its price, which is commonly known as HODL (jokingly interpreted as “hold on for dear life”). But your crypto is an asset and simply holding it is missing opportunities for it to earn interest. One of the most common ways to earn interest on your crypto is by staking tokens in a protocol that needs stakers as a means of verifying blocks on its blockchain via a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) protocol. Therein lies your opportunity to make your assets work for you.
What is Staking?
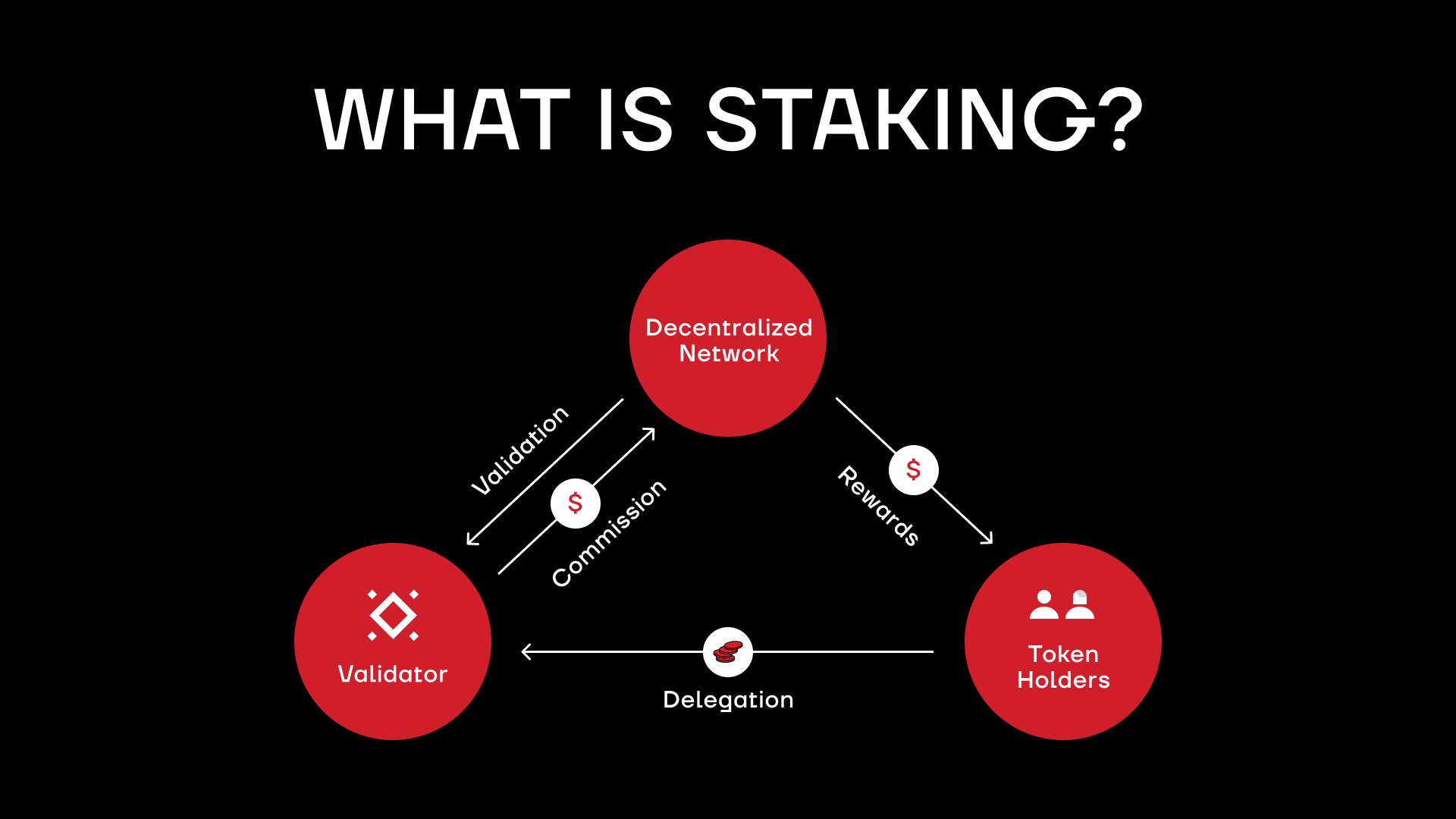
What does it mean to stake crypto? Staking is committing a specific amount of an asset for a certain period of time. Usually, your stake is locked for the entire period, aka it is considered to be in lockup. Staking is necessary to be a validator in a PoS system where it helps process blocks to add to the blockchain.
Mining vs Staking
So what does stake mean in crypto vs mining it, for example? Staking crypto isn’t the only way for blockchains to reach consensus in order to validate and add new blocks. Bitcoin, the original blockchain, is a Proof-of-Work (PoW) one and relies on mining. Miners are running powerful computers doing complex calculations on a specific math problem. The first one to solve it gets to validate the block and earn the reward for it. Unfortunately, mining is very costly in equipment investment and electricity costs, drawing the ire of environmentalists.
What is staking good for then? Proof-of-Stake saves up to 99% of electricity costs by simply allowing one to stake crypto meaning requiring validators to commit their coins to the protocol for the duration of their validator status. Those who prefer to earn by running hardware equipment and benefit from cheap electricity may prefer mining, while those who prefer to simply buy and hold the actual token tend to prefer staking.
How staking works?
How does staking work? How to stake crypto is actually relatively simple. In essence, stakers lock up a certain amount of crypto as collateral for being vested and honest validators. If they play by the rules and thus help properly validate blocks to add to the blockchain, they get rewarded with a portion of the transaction fees (commonly known as gas fees) that the network typically collects for every transaction that ends up being included in the block.
It is important to ensure proper behavior by validators because malicious actors could try to bribe validators to get their transactions ahead of other ones, which threatens the security of the network. Thus, stakers face a very real danger of losing their stake if they abuse their position of power. There are also mechanisms to randomize validators to make it harder for them to abuse the system or be targeted by malicious actors.
How Proof-of-Stake works?
How does staking crypto work in a PoS system? PoS is designed to reward those with the most at stake, aka those whose stake is the largest and committed for the longest time. The logic is basically: “if this person is putting up so much for a chance to validate blocks, they must really care about keeping this network secure and functioning.” Validator chosen in one round will not necessarily be chosen in the next.
The element of randomness gives more chances to smaller validators and limits the possibility for corruption. Though pooling tokens for a larger stake does increase chances of winning the right to validate each block, making staking coalitions a common phenomenon.

Staking Coins: Pros & Cons
Staking coins has its pros and cons that need to be considered.
Pros:
- With coin staking, you earn interest on your capital
- Get rewarded in the coin you already own
- Considered relatively safe: staking coin avoids impermanent loss associated with yield farming
- Participate in the security and growth of the network
Cons:
- While your coin is locked up, its market value could plummet and you won’t be able to sell it in time
- Staking crypto meaning that you’re not doing something else with it, thus it is often less lucrative than the more risky yield farming and landing
- Purchasing enough coins for a stake may be unaffordable for many investors

Which Tokens Can you Stake?
Some of the most commonly staked tokens are Ethereum, Tezos, Cardano, Cosmos, Polkadot, and EOS. But there are new PoS blockchains popping up all the time. Just make sure you are staking a coin that can be staked. For example, can you stake bitcoin? The short answer is not really since you cannot stake bitcoin to validate the bitcoin blockchain since it’s a PoW system. Though staking bitcoin may be possible on other platforms that want to use bitcoin staking for purposes other than securing the bitcoin blockchain. So if you want to stake cryptocurrency and are not sure if it’s possible, do some digging, because you never know what new staking mechanism just became available.

Where Can I Stake?
Each blockchain with a PoS protocol has its own staking website where they explain the ways to stake coins and maybe even offer staking right there. Take the one for Ethereum as an example. The website talks about the various options of staking ETH, including solo staking at home, pooled staking, centralized exchange (CEX) staking, and Staking-as-a-Service:
Solo Staking
What does stake crypto mean for individuals? In the case of Ethereum, if you have at least 32 ETH, you can become a validator on your own, without paying fees to somebody to set up or run it for you or letting your funds out of your direct custody. You will need to have a dedicated computer connected to the Internet 24/7. This is how PoS was meant to work. But since a lot of people can’t meet these requirements, other options exist.
Pooled Staking
How do you stake crypto if you don’t have enough for a node? And what is crypto staking jointly with others? Pooled staking protocols, like Rocket Pool or Lido (which calls it “liquid staking”), allow people to stake with smaller amounts of ETH and a lot more convenience (with options to not even run a node — for a lower APR). The tradeoffs are having to pay fees (and thus getting a lower APR) and, in some cases, having to give up custody of your ETH to the pool.
Staking-as-a-Service (SaaS)
What is staking crypto as a service? If you do have enough tokens to run a validator node (e.g. 32 ETH) you can use a SaaS provider (BoxStaking, Abyss Finance, etc.) that will walk you through the difficult part of setting up and running a node while avoiding the mixing of your funds with others. It’s very convenient to have crypto staking explained to you. You will sometimes have to custody your funds with the provider but many will give you the only “copy” of the keys to withdraw them to minimize trust issues (or are noncustodial to begin with).
CEX staking
What does staking crypto mean on a CEX? Perhaps the easiest way to stake is via a centralized exchange where you already have your crypto to begin with. Major exchanges like Coinbase and Binance have staking reduced to a couple of clicks (so check out their sites if you want to know how to stake on coinbase or binance). Of course, any funds you keep on a CEX follows the “not your keys not your crypto” maxim.
Start staking in 5 steps
Now that you know the basics of staking and the staking options, you may be aching to just go ahead and stake. After all, what is staking in crypto if you don’t actually do it? But this may seem overwhelming with so many options. Let’s reduce it to 5 simple steps one may take:
- Buy whichever token you want to stake
- Choose between solo, pooled, SaaS, and CEX staking
- Choose provider (use a site like CryptoTesters to compare)
- Follow the instructions to start staking
- Check in periodically to make sure your earnings match what was advertised

Choosing a Staking Platform
When deciding on which staking platform to choose, one should consider a number of factors, including the potential return rate, the platform’s reputation, lockup/custodianship of funds, ease of use, etc. What does staked mean exactly on that specific platform?
Luckily, there are sites that make it their job to compare platforms, such as CryptoTesters for ETH, ZenLedger for Cardano, and many others. Just remember that there is no guarantee that any reviews or rankings are truly unbiased. Always DYOR and protect your capital

Staking On a Hardware Wallet
How does crypto staking work for hardware wallets? If you keep your funds on a cold storage hardware wallet such as Ledger or Trezor, you can still stake your tokens while maintaining the security that hardware wallets are known for. There are even tutorials on how to stake, like this one from Weirdo Rocks.

Is Crypto Staking Profitable?
What does staking mean for profitability considerations? Profitability of anything tends to vary. Because staking is usually done in a single cryptocurrency and the return is in the same one, staking is profitable relative to that currency. For example, if you stake ETH and receive a little extra ETH back every second, you’re net positive on ETH.
On the other hand, that currency itself can lose value either due to temporary price volatility or bigger market movements. This is especially true if the currency is inflationary (which usually happens as more of a currency gets minted than there is demand for it). Ethereum is trying to become deflationary by burning some ETH in gas fees but it is still inflationary as new ETH keeps getting created.
There is also the matter of relative profitability when staking cryptocurrency since your capital can always be used to generate income somewhere else, whether in yield farming, lending, blockchain gaming, trading, or a number of other strategies. So you need to be mindful of the opportunity costs.
Lastly, don’t ignore the fees and other associated costs. While staking uses only a fraction of electricity and processing power compared to mining, there are still physical and time costs to consider as part of the profitability equation.

What are some staking risks?
As mentioned above, there are several risks associated with staking your crypto. For one, locking an asset up means you can’t quickly move it when you urgently need liquidity or trade it should the price plummet. The other risk, specific to custodial staking services, is that you will lose access to your funds from a number of unforeseen events such as the service getting hacked, collapsing, or being ordered by government regulators to freeze your assets. A crypto exchange is not a bank, and even regulated ones may not get your staked crypto back in cases of hacking or government action.
To be fair, some cryptocurrency staking services are non-custodial or provide other assurances that only you can access your money. And since staking often attracts crypto HODLers, temporary price pullbacks may not matter as much anyway.

The Future of Crypto Staking
So that’s where crypto staking is at today. But where will it go tomorrow, next year, or in a decade? No one knows for sure, but certain developments are quite possible. So let’s speculate. Maybe staking will be rewarded in new ways such as with exclusive NFTs, whitelist access, aidrops, and bonus yield from partner protocols. Some of this is already being implemented here and there. Maybe there will be staking-based derivatives traded on various markets. Maybe even in betting markets. It would be very interesting to see staking expanded outside of DeFi into all realms of our lives. Imagine citizens staking their votes and thus influencing government action.
As crypto becomes more and more mainstream and PoS proves itself, staking may take on an even more prominent role. And now you know how to get started, your options, and what to keep in mind.










